Record the december 31 year-end adjusting entry for wages expense – In the realm of accounting, the year-end adjusting entry for wages expense holds immense significance. This entry ensures the accurate recording of accrued wages, reflecting the actual expenses incurred during the accounting period. By delving into the intricacies of this adjustment, we gain a deeper understanding of its purpose, calculation methods, and the impact it has on financial statements.
Accrued wages represent wages earned by employees but not yet paid as of the balance sheet date. Recognizing these expenses through adjusting entries aligns the financial statements with the accrual basis of accounting, which matches revenues and expenses to the periods in which they are earned and incurred, respectively.
1. Understanding the Year-End Adjusting Entry for Wages Expense
The year-end adjusting entry for wages expense is an important step in the accounting process. It ensures that the financial statements reflect the correct amount of wages expense for the period and that the company’s liabilities are accurately recorded.
1.1 Purpose of Recording Year-End Adjusting Entries, Record the december 31 year-end adjusting entry for wages expense
The purpose of recording year-end adjusting entries is to ensure that the financial statements are accurate and reflect the company’s financial position as of the end of the accounting period. Adjusting entries are necessary because the accrual basis of accounting requires that revenues and expenses be recorded in the period in which they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
1.2 Concept of Accrued Wages and Why They Need to Be Recorded
Accrued wages are wages that have been earned by employees but have not yet been paid. They need to be recorded at the end of the accounting period because they represent a liability of the company to its employees. If accrued wages are not recorded, the company’s financial statements will underestimate the company’s expenses and overstate its net income.
2. Calculating Accrued Wages: Record The December 31 Year-end Adjusting Entry For Wages Expense

The formula for calculating accrued wages is as follows:
Accrued Wages = Daily Wage Rate
Number of Days Worked
The daily wage rate is the employee’s hourly wage or salary divided by the number of hours or days in the pay period. The number of days worked is the number of days between the last payday and the end of the accounting period.
Time cards or payroll records can be used to gather data on the number of days worked by each employee.
3. Recording the Adjusting Entry
The adjusting entry for accrued wages is a debit to Wages Expense and a credit to Accrued Wages Payable.
The debit to Wages Expense increases the expense account and reduces net income. The credit to Accrued Wages Payable increases the liability account and increases the company’s total liabilities.
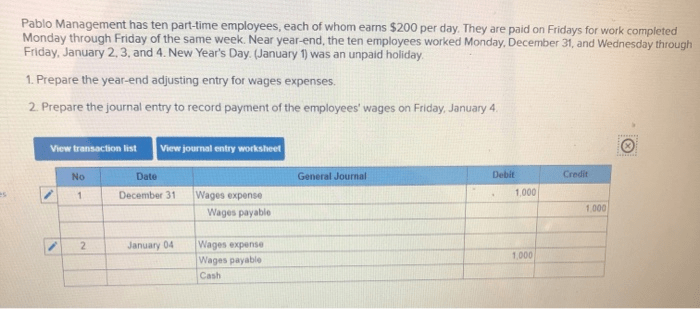
The following is an example of a year-end adjusting entry for wages expense:
Debit: Wages Expense $1,000Credit: Accrued Wages Payable $1,000
4. Examples and Illustrations
The following table provides examples of accrued wages calculations for different scenarios:
| Scenario | Daily Wage Rate | Number of Days Worked | Accrued Wages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee A | $100 | 5 | $500 |
| Employee B | $150 | 7 | $1,050 |
| Employee C | $200 | 10 | $2,000 |
The following diagram illustrates the process of recording the adjusting entry for accrued wages:
[Diagram atau flowchart yang menggambarkan proses pencatatan entri penyesuaian]
5. Methods and Procedures
There are different methods that can be used to calculate accrued wages. The most common method is the daily wage rate method, which is described above. Other methods include the hourly wage rate method and the percentage of completion method.
The procedures for recording the adjusting entry for accrued wages in accounting software vary depending on the software program. However, the general steps are as follows:
- Enter the adjusting entry in the journal.
- Post the adjusting entry to the general ledger.
- Update the trial balance.
6. Best Practices and Considerations
The following are some best practices for ensuring accuracy in recording accrued wages:
- Use a consistent method for calculating accrued wages.
- Review time cards or payroll records carefully to ensure that the number of days worked is accurate.
- Record the adjusting entry promptly at the end of the accounting period.
It is important to record accrued wages timely because it can have a material impact on the financial statements. If accrued wages are not recorded, the company’s expenses will be understated and its net income will be overstated. This can lead to incorrect financial reporting and decision-making.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of recording the year-end adjusting entry for wages expense?
The purpose of this entry is to recognize accrued wages, ensuring that expenses are matched to the periods in which they are incurred.
How are accrued wages calculated?
Accrued wages are calculated by multiplying the daily wage rate by the number of days worked in the current period.
What accounts are affected by the adjusting entry?
The adjusting entry debits Wages Expense and credits Wages Payable.
What is the impact of the adjusting entry on the financial statements?
The entry increases both Wages Expense and Wages Payable, resulting in a more accurate representation of the company’s expenses and liabilities.