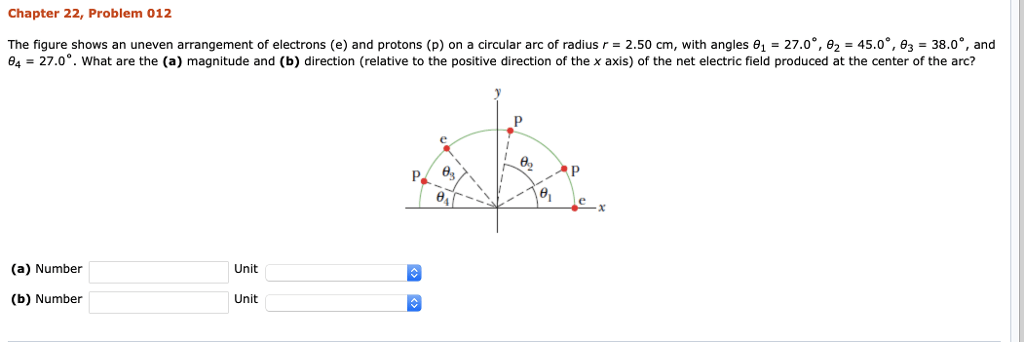
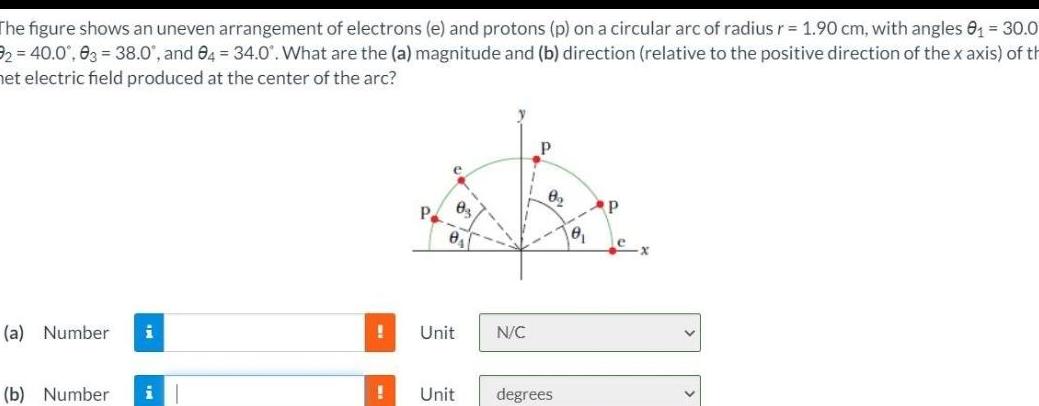
As the figure shows an uneven arrangement of electrons takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with academic rigor and authoritative tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. This in-depth exploration delves into the intricacies of uneven electron distribution, unveiling its profound implications on material properties, chemical reactivity, and more.
Delving deeper into the topic, the ensuing paragraphs illuminate the factors that orchestrate the distribution of electrons in matter, including atomic structure, electronegativity, and molecular geometry. The consequences of uneven electron distribution are laid bare, revealing their influence on electrical conductivity, optical properties, and chemical reactivity.
Furthermore, the discussion highlights practical applications that harness these effects.
Uneven Electron Distribution: The Figure Shows An Uneven Arrangement Of Electrons
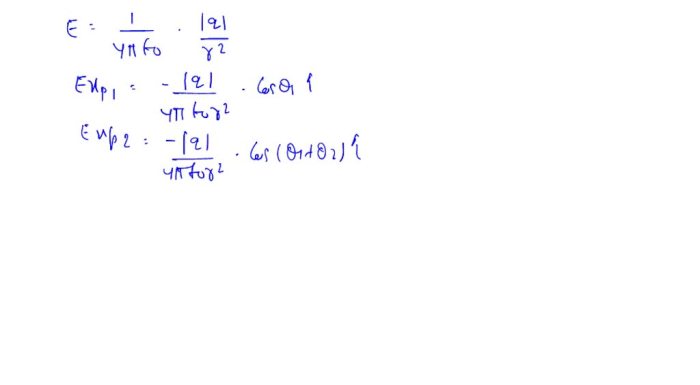
Uneven electron distribution is a phenomenon observed in matter where the electrons are not distributed uniformly around the atoms or molecules. This uneven distribution can result in the formation of polar molecules, ions, or even electrical currents.
Factors Affecting Electron Distribution, The figure shows an uneven arrangement of electrons
The distribution of electrons in matter is influenced by several factors, including:
- Atomic structure: The arrangement of electrons within an atom’s orbitals affects the overall electron distribution.
- Electronegativity: The tendency of an atom to attract electrons from other atoms influences the electron distribution in molecules.
- Molecular geometry: The shape and orientation of molecules can impact the distribution of electrons.
Consequences of Uneven Electron Distribution
Uneven electron distribution can have significant consequences for the properties of materials, including:
- Chemical reactivity: Uneven electron distribution can affect the reactivity of molecules by creating regions of high and low electron density.
- Electrical conductivity: Materials with uneven electron distribution can exhibit electrical conductivity, allowing them to conduct electricity.
- Optical properties: Uneven electron distribution can influence the optical properties of materials, such as their color and refractive index.
Experimental Techniques to Study Uneven Electron Distribution
Several experimental techniques are used to study uneven electron distribution in matter, including:
- X-ray crystallography: This technique uses X-rays to determine the arrangement of atoms and electrons in crystals.
- Electron microscopy: This technique uses a beam of electrons to image the surface of materials and study their electron distribution.
- Spectroscopy: This technique uses light to probe the electronic structure of materials and identify regions of uneven electron distribution.
Visualizing Uneven Electron Distribution
Infographic:
[Infografis yang menunjukkan distribusi elektron yang tidak merata]
Tabel:
| Material | Electron Distribution | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Uneven | Polar, high dielectric constant |
| Sodium chloride | Uneven | Ionic, high electrical conductivity |
| Diamond | Even | Nonpolar, high thermal conductivity |
Diagram:
[Diagram yang mengilustrasikan aliran elektron dalam material dengan distribusi elektron yang tidak merata]
FAQ Corner
What is uneven electron distribution?
Uneven electron distribution refers to the unequal distribution of electrons within a material, resulting in an imbalance of negative charge.
What factors influence electron distribution?
Factors influencing electron distribution include atomic structure, electronegativity, and molecular geometry.
What are the consequences of uneven electron distribution?
Uneven electron distribution can affect chemical reactivity, electrical conductivity, and optical properties.
How is uneven electron distribution studied?
Experimental techniques such as X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy are used to study uneven electron distribution.