What is the acceleration of the 2.0 kg block – In the realm of physics, the acceleration of the 2.0 kg block stands as a pivotal concept, inviting us to delve into the intricacies of motion and the forces that govern it. This discourse will illuminate the essence of acceleration, unraveling its relationship with velocity and displacement, and showcasing its ubiquitous presence in our everyday experiences.
Newton’s second law of motion emerges as a cornerstone in our quest to understand acceleration. We will explore how this fundamental principle enables us to quantify acceleration and unravel its significance in solving real-world problems.
1. Overview
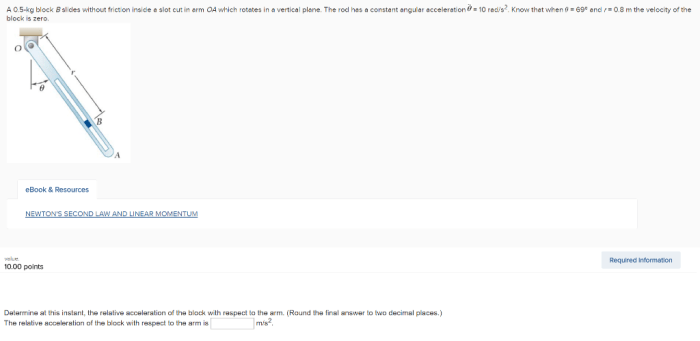
Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2), and the direction is the direction in which the object is accelerating.
Acceleration is related to velocity and displacement by the following equations:
- Acceleration = (Final velocity – Initial velocity) / Time
- Final velocity = Initial velocity + Acceleration – Time
- Displacement = Initial position + (Initial velocity – Time) + (0.5 – Acceleration – Time^2)
Examples of acceleration in everyday life include:
- A car speeding up from a stoplight
- A ball falling from a height
- A person running a race
2. Newton’s Second Law
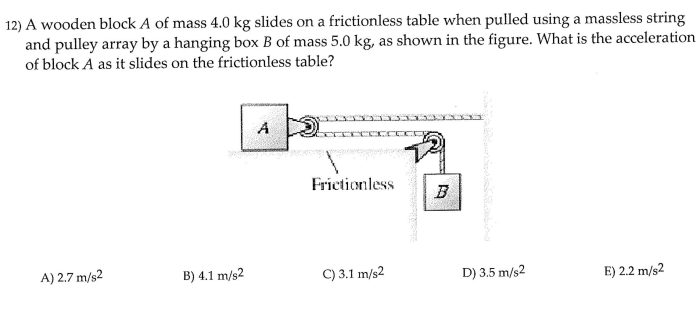
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
F = ma
Where:
- F is the net force acting on the object (in newtons)
- m is the mass of the object (in kilograms)
- a is the acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
Newton’s second law can be used to calculate the acceleration of an object by rearranging the equation to:
a = F / m
Examples of how Newton’s second law is used to solve problems include:
- Calculating the acceleration of a car given the force applied to the car and the mass of the car
- Calculating the acceleration of a ball given the force of gravity acting on the ball and the mass of the ball
- Calculating the acceleration of a person given the force applied to the person and the mass of the person
3. Free Fall
Free fall is a type of motion in which an object is only subject to the force of gravity. In free fall, the acceleration of the object is equal to the acceleration due to gravity, which is approximately 9.8 m/s^2 on Earth.
Examples of free fall include:
- A ball falling from a height
- A person skydiving
- A raindrop falling from the sky
4. Inclined Planes
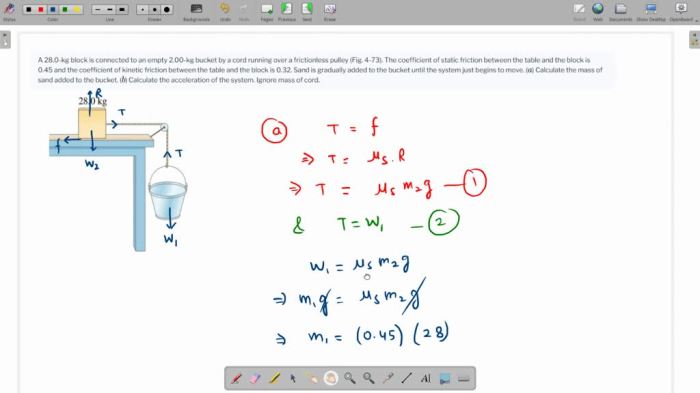
An inclined plane is a sloping surface. When an object is placed on an inclined plane, it is subject to the force of gravity and the normal force of the plane.
The acceleration of an object on an inclined plane can be calculated using the following equation:
a = g- sin(theta)
Where:
- a is the acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (in meters per second squared)
- theta is the angle of the inclined plane (in degrees)
Examples of objects moving on inclined planes include:
- A ball rolling down a hill
- A car driving up a ramp
- A person walking up a flight of stairs
5. Circular Motion
Circular motion is a type of motion in which an object moves in a circle. In circular motion, the object is subject to a centripetal force, which is a force that points towards the center of the circle.
The centripetal acceleration of an object in circular motion can be calculated using the following equation:
a = v^2 / r
Where:
- a is the centripetal acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
- v is the speed of the object (in meters per second)
- r is the radius of the circle (in meters)
Examples of circular motion include:
- A car driving around a curve
- A ball spinning on a string
- A person swinging on a swing
Commonly Asked Questions: What Is The Acceleration Of The 2.0 Kg Block
What is acceleration?
Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time, encompassing both the magnitude and direction of the change.
How is acceleration calculated using Newton’s second law?
Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass, expressed as a = F/m.
What is free fall?
Free fall describes the motion of an object solely under the influence of gravity, experiencing an acceleration due to gravity of approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth.